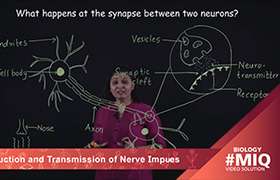
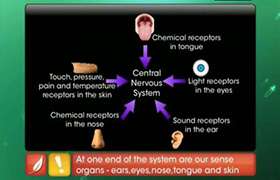
CBSE Class 10 Answered
Food and oxygen are carried to the brain by many blood vessels. These vessels are found on the surface of the brain and deep within the brain.
Although the brain is only about 2% of the total body weight in humans, it receives 15-20% of the body's blood supply.
Blood is supplied to the entire brain by 2 pairs of arteries: the internal carotid arteries and vertebral arteries. The right and left vertebral arteries come together at the base of the brain to form a single basilar artery. The basilar artery joins the blood supply of the internal carotid arteries in a ring at the base of the brain.
Because brain cells will die if the supply of blood which carries oxygen is stopped, the brain has top priority for the blood. Even if other organs need blood, the body attempts to supply the brain with a constant flow of blood.A stroke occurs when blood supply to the brain is stopped. If this happens for enough time, neurons will start to die because they will not get enough oxygen. Paralysis or aphasia (loss of speech) are possible consequences of a stroke.
The midbrain consists of the tectum and tegmentum.
Diencephalon, the third part of forebrain, is a small structure hidden below the cerebrum. It is divided into thalamus and hypothalamus.
The thalamus is situated below the corpus callosum. The roof of the thalamus is called epithalamus. The anterior part of the epithalamus is called anterior choroid plexus, which secretes cerebrospinal fluid. The pineal body is situated on the roof of the thalamus, which secretes hormone melatonin. The subthalamus is located directly lower of the thalamus and includes the subthalamic nuclei, parts of the red nuclei, and the substantia nigra. In correlation with these three parts they communicate with the basal ganglia to help control body movement
Thalamus is a major coordinating center for sensory and motor signaling. Its complex neural circuits sort the incoming stimuli. Melatonin influences sleep-wake cycles and other circadian rhythms.
Hypothalamus is located at the base of thalamus. The hypothalamus contains several groups of neurosecretory cells, which secrete the hypothalamic hormones.
The hypothalamus controls the involuntary activities of the body. It contains a number of centres which control thermo-regulation and feelings of hunger and thirst. The hypothalamus, along with the limbic system is invoved in the regulation of sexual behaviour, expression of emotional reactions and motivation.