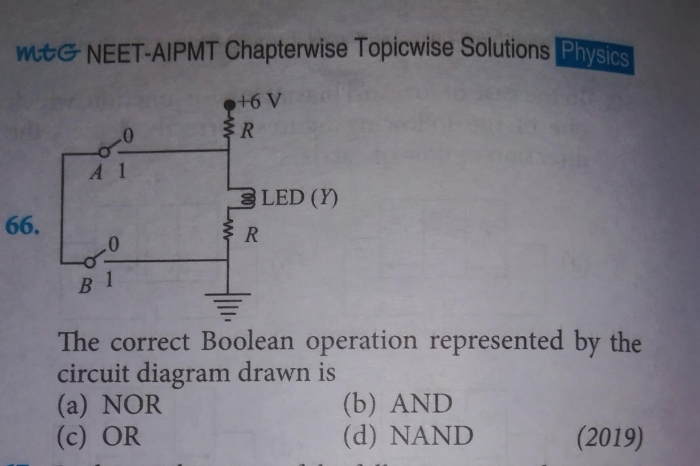
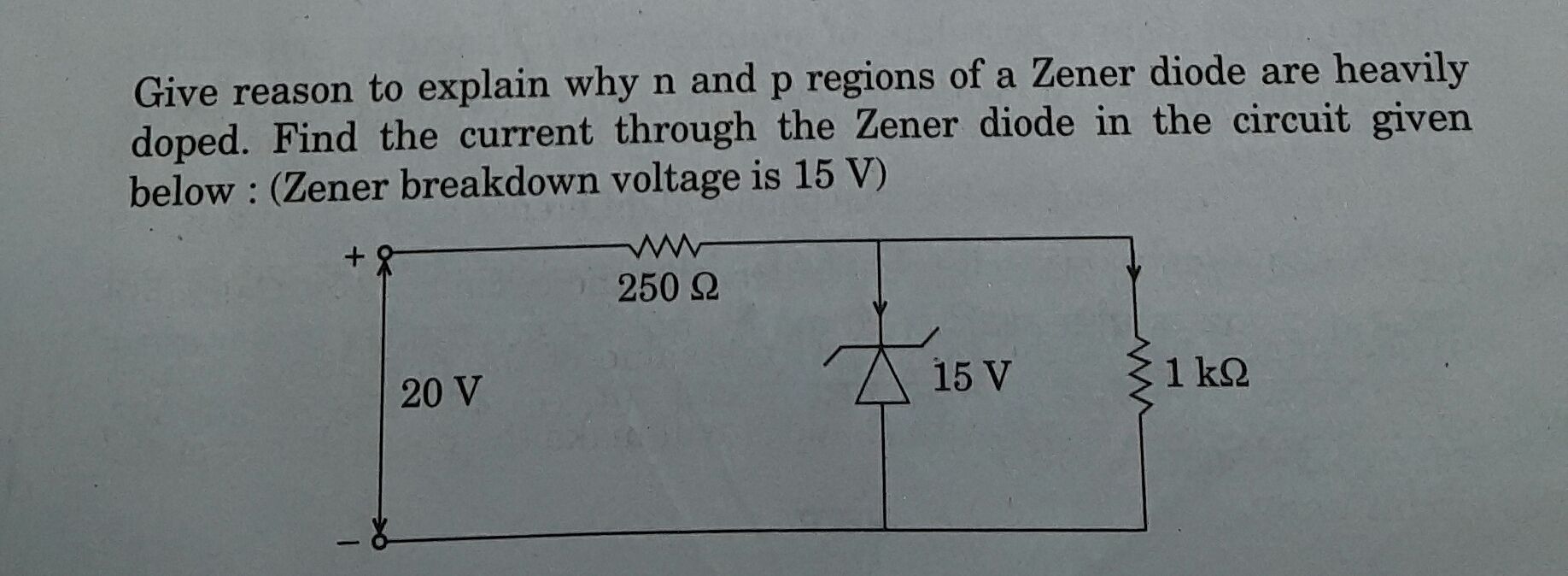
CBSE Class 12-science Answered
A Single Capacitor


If we place a capacitor at the output of the full-wave rectifier as shown to the left, the capacitor will charge to the peak voltage each half-cycle, and then will discharge more slowly through the load while the rectified voltage drops back to zero before beginning the next half-cycle. Thus, the capacitor helps to fill in the gaps between the peaks, as shown in red in the first figure to the right.
Although we have used straight lines for simplicity, the decay is actually the normal exponential decay of any capacitor discharging through a load resistor. The extent to which the capacitor voltage drops depends on the capacitance of the capacitor and the amount of current drawn by the load; these two factors effectively form the RC time constant for voltage decay.

As a result, the actual voltage output from this combination never drops to zero, but rather takes the shape shown in the second figure to the right. The blue portion of the waveform corresponds to the portion of the input cycle where the rectifier provides current to the load, while the red portion shows when the capacitor provides current to the load. As you can see, the output voltage, while not pure dc, has much less variation (or ripple, as it is called) than the unfiltered output of the rectifier.
A half-wave rectifier with a capacitor filter will only recharge the capacitor on every other peak shown here, so the capacitor will discharge considerably more between input pulses. Nevertheless, if the output voltage from the filter can be kept high enough at all times, the capacitor filter is sufficient for many kinds of loads, when followed by a suitable regulator circuit.
LC Filters

While the RC filter shown above helps to reduce the ripple voltage, it introduces excessive resistive losses when the load current is significant. To reduce the ripple even more without a lot of dc resistance, we can replace the resistor with an inductor as shown in the circuit diagram to the right.
In this circuit, the two capacitors store energy as before, and attempt to maintain a constant output voltage between input peaks from the rectifier. At the same time, the inductor stores energy in its magnetic field, and releases energy as needed in its attempt to maintain a constant current through itself. This provides yet another factor that attempts to smooth out the ripple voltage.
In some cases, C1 is omitted from this filter circuit. The result is a lower dc output voltage, but improved ripple removal. The choice is a trade-off, and must be made according to the specific requirements in each individual case.
For dc, the inductance has only the resistance of the wire that comprises the coil, which amounts to a few ohms. Meanwhile, the capacitors still operate as open circuits at dc, so they do not reduce the dc output voltage. However, at the basic ripple frequency of 120 Hz, a 10 Henry inductance has a reactance of:
At the same time, a 100 µf capacitor at the same ripple frequency has a reactance of:
Thus, L and C2 form a voltage divider that drastically reduces the ripple component (to less than 0.2%) while leaving the desired dc output nearly alone. This configuration may provide sufficiently pure dc for some applications, without the need for any following regulator at all.
The drawback of this approach is that a 10 Henry inductor is as large as some power transformers, with a heavy iron core. It takes up a lot of space and is relatively expensive. This is why the RC filter circuit may be preferred to the LC filter, provided the ripple reduction is sufficient and the power loss in the resistor is not excessive.