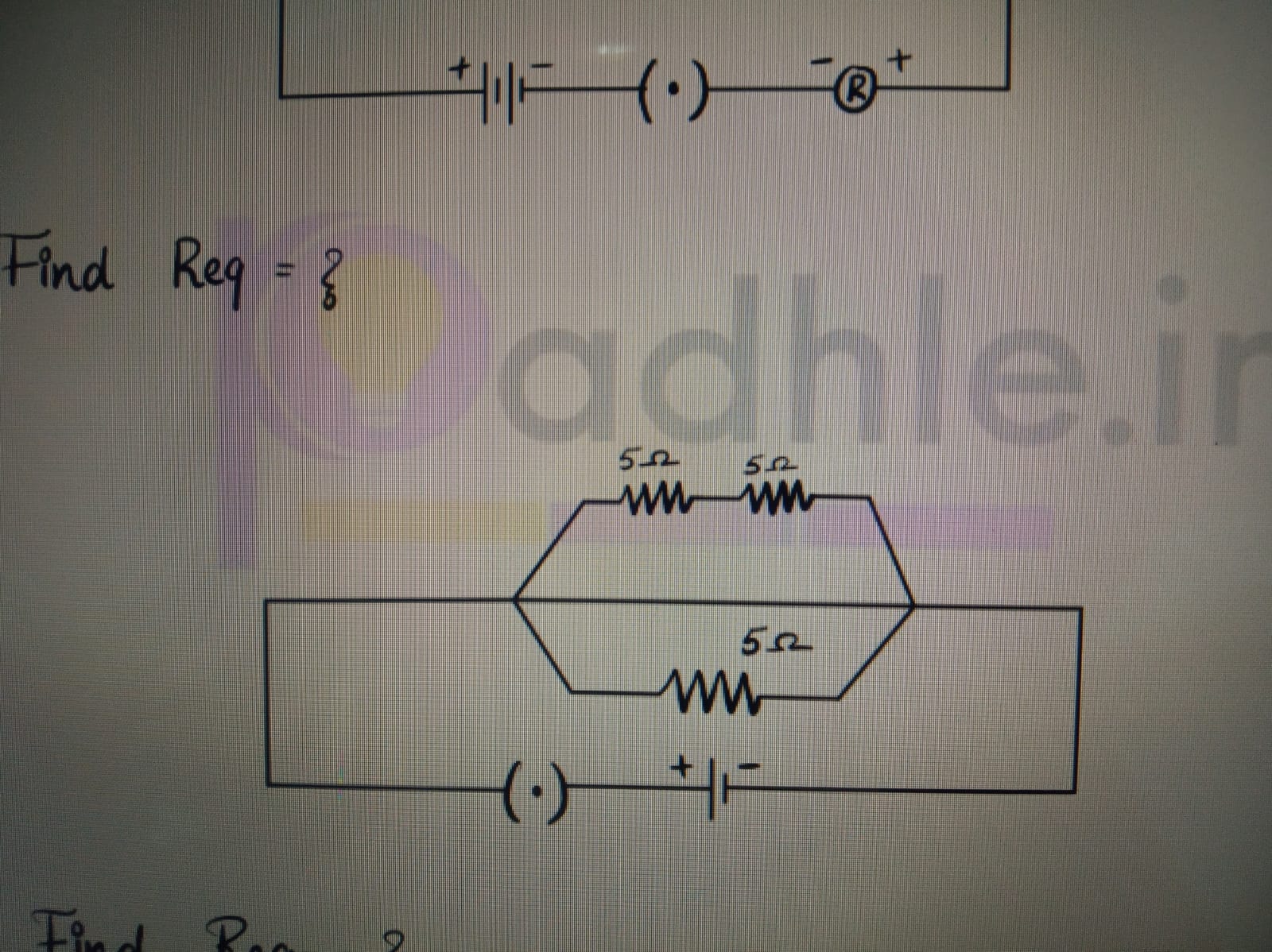
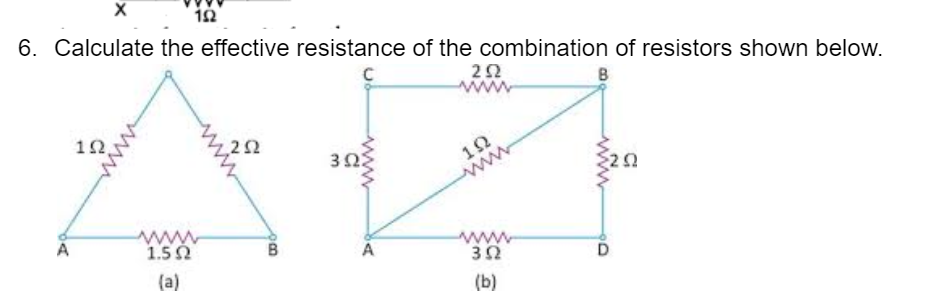
CBSE Class 10 Answered
give the derivation of resultant power in series and parallel
Asked by rishabh trehan | 16 May, 2013, 07:09: PM
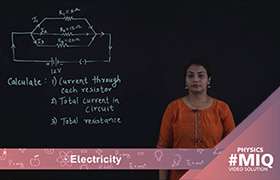
P = I^2 * R or V^2/R
For a series connection with resistors R1, R2, R3...etc connected in series
R = R1+R2+R3+ ....
And the current in this circuit remains constant,
so, P = I^2 ( R1+R2+R3+ ....)
For a parallel connection with resistors R1, R2, R3...etc connected in parallel
1/R = 1/R1+1/R2+1/R3+ ....
And the voltage drop in this circuit remains constant,
so, P = V^2 /( 1/R1+1/R2+1/R3+ ....)
Answered by | 16 May, 2013, 09:31: PM
Application Videos
Concept Videos
CBSE 10 - Physics
Asked by khajannirwan | 27 Feb, 2024, 10:20: PM
CBSE 10 - Physics
Asked by saanviyadla | 24 Jan, 2024, 07:06: PM
CBSE 10 - Physics
Asked by kamalaranjanmohantymohanty5 | 06 Jan, 2024, 10:05: AM
CBSE 10 - Physics
Asked by nandhikasugumar | 05 Oct, 2023, 04:01: PM
CBSE 10 - Physics
Asked by daniya062008 | 02 Oct, 2023, 08:25: PM
CBSE 10 - Physics
Asked by prassanna.j | 03 Sep, 2023, 12:28: PM
CBSE 10 - Physics
Asked by prassanna.j | 03 Sep, 2023, 12:21: PM
CBSE 10 - Physics
Asked by prassanna.j | 03 Sep, 2023, 12:13: PM
CBSE 10 - Physics
Asked by prassanna.j | 03 Sep, 2023, 12:11: PM