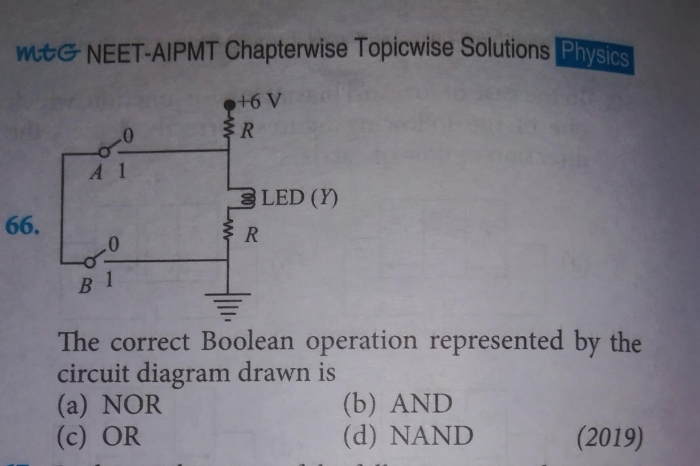
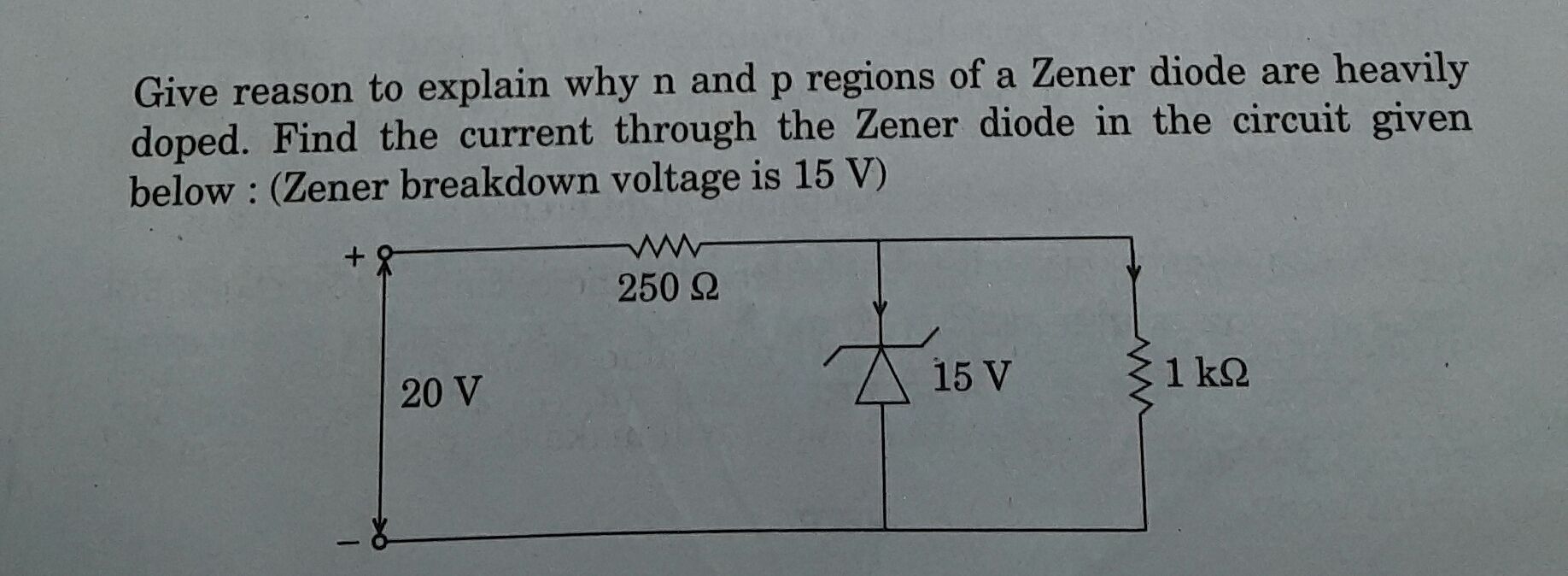
CBSE Class 12-science Answered
The Transistor as an Amplifier
Amplification is the process of linearly increasing the amplitude of an electrical signal.
A transistor can act as an amplifier directly using the gain, b.
Keep in mind that when a transistor is biased in the active (linear) region, the BE junction has a low resistance due to forward bias and the BC junction has a high resistance due to reverse bias.
i) DC and AC quantities
Amplifier circuits have both ac and dc quantities.
Capital letters are used will be used for both ac and dc currents.
Subscript will be capital for dc quantities.
Subscript will be lowercase for ac quantities.
ii) Transistor amplification
A transistor amplifies current because the collector current is equal to the base current multiplied by the current gain, b.
Base current (IB) is small compared to IC and IE.
Thus, IC is almost equal to IE.