CBSE Class 12-science Answered
explain the formation of mature embryo from embry sac?
Asked by vasturushi | 02 Jun, 2017, 10:50: PM
The development of an embryo from a zygote is called embryogeny. The development takes place at the micropylar end of the embryo sac. Most of the zygotes divide only after a certain amount of endosperm is formed. This provides assured nourishment to the developing embryo.
Development of Embryo in Dicots:
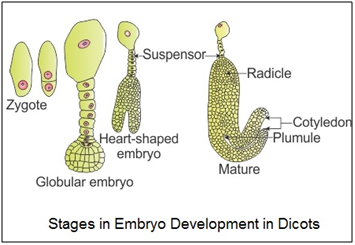
- The zygote divides into two unequal cells, larger suspensor cell towards the micropyle and a smaller embryonal cell towards the antipodal region.
- The suspensor cell undergoes transverse division to form 6-10 celled suspensor.
- The suspensor cell towards the micropylar end is large and is called haustorium or vesicular cell.
- The suspensor cell towards the embryonal cell is called hypophysis which forms the radicle tip.
- The embryonal cell divides twice vertically and once transversely to produce a two-tiered eight-celled embryo.
- The epibasal tier forms two cotyledons and a plumule while the hypobasal tier produces only hypocotyl and most of the radicle.
- The octant embryo undergoes periclinal divisions to produce protoderm, procambium and ground meristem.
- Protoderm forms epidermis, procambium forms stele and ground meristem produces cortex and pith.
- Initially, the embryo is globular and undifferentiated and is called proembryo.
- It is then transformed into embryo with the development of radicle, plumule and cotyledons.
Answered by Sheetal Kolte | 03 Jun, 2017, 12:45: PM
Concept Videos
CBSE 12-science - Biology
Asked by ishtiyaqishuuu | 30 Jan, 2023, 11:15: AM
CBSE 12-science - Biology
Asked by viratsingh73558 | 26 Dec, 2022, 08:08: PM
CBSE 12-science - Biology
Asked by carnivalgirl8421 | 30 Jun, 2022, 02:28: PM
CBSE 12-science - Biology
Asked by carnivalgirl8421 | 30 Jun, 2022, 01:58: PM
CBSE 12-science - Biology
Asked by sunidhichauhan3625 | 10 Jun, 2022, 03:48: PM
CBSE 12-science - Biology
Asked by imran.jr | 03 Sep, 2020, 10:13: PM
CBSE 12-science - Biology
Asked by dasneeraj36 | 19 May, 2020, 07:47: PM
CBSE 12-science - Biology
Asked by Aayushsharma1617 | 27 Jun, 2019, 09:57: AM
CBSE 12-science - Biology
Asked by gganga | 21 Jun, 2018, 07:18: PM
CBSE 12-science - Biology
Asked by Topperlearning User | 11 Jun, 2014, 04:47: PM