CBSE Class 11-science Answered
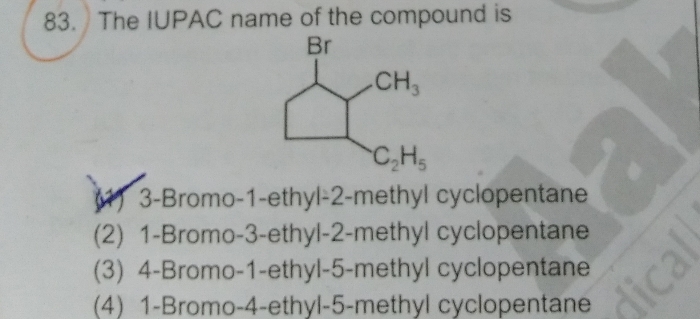
explain the electron displacement effect in covalent bond ?
Asked by dileepkumar | 18 Dec, 2012, 08:32: PM
Electronic displacement in covalent bonds
It is observed that most of the attacking reagents always possess either a positive or a negative charge, therefore for a reaction to take place on the covalent bond the latter must possess oppositely charged centres. This is made possible by displacement (partial or complete) of the bonding electrons. The electronic displacement in turn may be due to certain effects, some of which are permanent and others are temporary. The former effects are permanently operating in the molecule and are known aspolarization effects, while the latter are brought into play by the attacking reagent and as soon as the attacking reagent is removed, the electronic displacement disappears; such effects are known as thepolarisability effects.

Answered by | 19 Dec, 2012, 09:09: AM
Concept Videos
CBSE 11-science - Chemistry
Asked by josephineanto1960 | 28 Mar, 2024, 12:50: PM
CBSE 11-science - Chemistry
Asked by neet2025targetgo | 25 Mar, 2024, 10:13: AM
CBSE 11-science - Chemistry
Asked by ap4450962 | 12 Mar, 2024, 07:35: PM
CBSE 11-science - Chemistry
Asked by pamjat.8888 | 31 Jan, 2024, 11:31: AM
CBSE 11-science - Chemistry
Asked by sahumahesh3973 | 20 Jan, 2024, 06:33: PM
CBSE 11-science - Chemistry
Asked by aswintj2007 | 07 Jan, 2024, 08:53: PM
CBSE 11-science - Chemistry
Asked by dipalisingh0908 | 05 Nov, 2023, 02:24: PM
CBSE 11-science - Chemistry
Asked by badalbehera258369 | 19 Oct, 2023, 02:01: PM
CBSE 11-science - Chemistry
Asked by prakrutikhosla | 16 Sep, 2023, 06:31: PM
CBSE 11-science - Chemistry
Asked by shahintkjnv2016 | 13 Jun, 2022, 07:17: PM