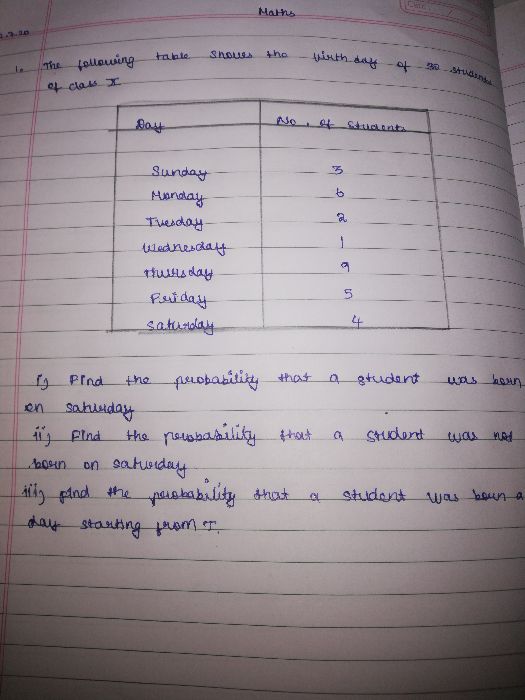
CBSE Class 9 Answered
1) Probability is a quantitative measure of certainty. For example the probability of getting a head when a coin is tossed is ½.
2) Any particular performance of a random experiment is called a trial. By Experiment or Trial in the subject of probability, we mean a Random experiment unless otherwise specified.
Each trial results in one or more outcomes
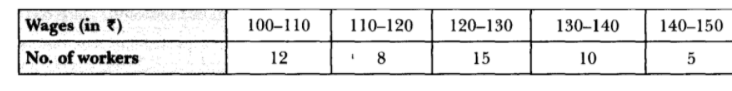
Example: tossing a coin, Picking 2 balls from a bag containing 15 balls 9 of which are red and 6 blue
3) If an experiment, when repeated under identical conditions, do not produce the same outcome every time but the outcome in a trial is one of the several possible outcomes, then it is known as a random or probabilistic experiment.
Example of random experiments:
(i) Tossing a fair coin
(ii) Rolling an unbiased die
(iii) Drawing a card from a well shuffled pack of cards
4) The collection of all possible outcomes is called the sample space.
Example: In a single throw of a die, the possible outcomes are 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 or 6. Thus, the sample space for rolling a die is {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6}
5) An outcome of a random experiment is called an elementary event.
Example: Consider the random experiment of tossing of a coin. The possible outcomes of this experiment are head (H) or tail (T).
6) An event associated to a random experiment is a compound event if it is obtained by combining two or more elementary events associated to the random experiment.
Example: In a single throw of a die, the event "Getting an odd number" is a compound event as it is obtained by combining three elementary events, namely, 1, 3, 5.