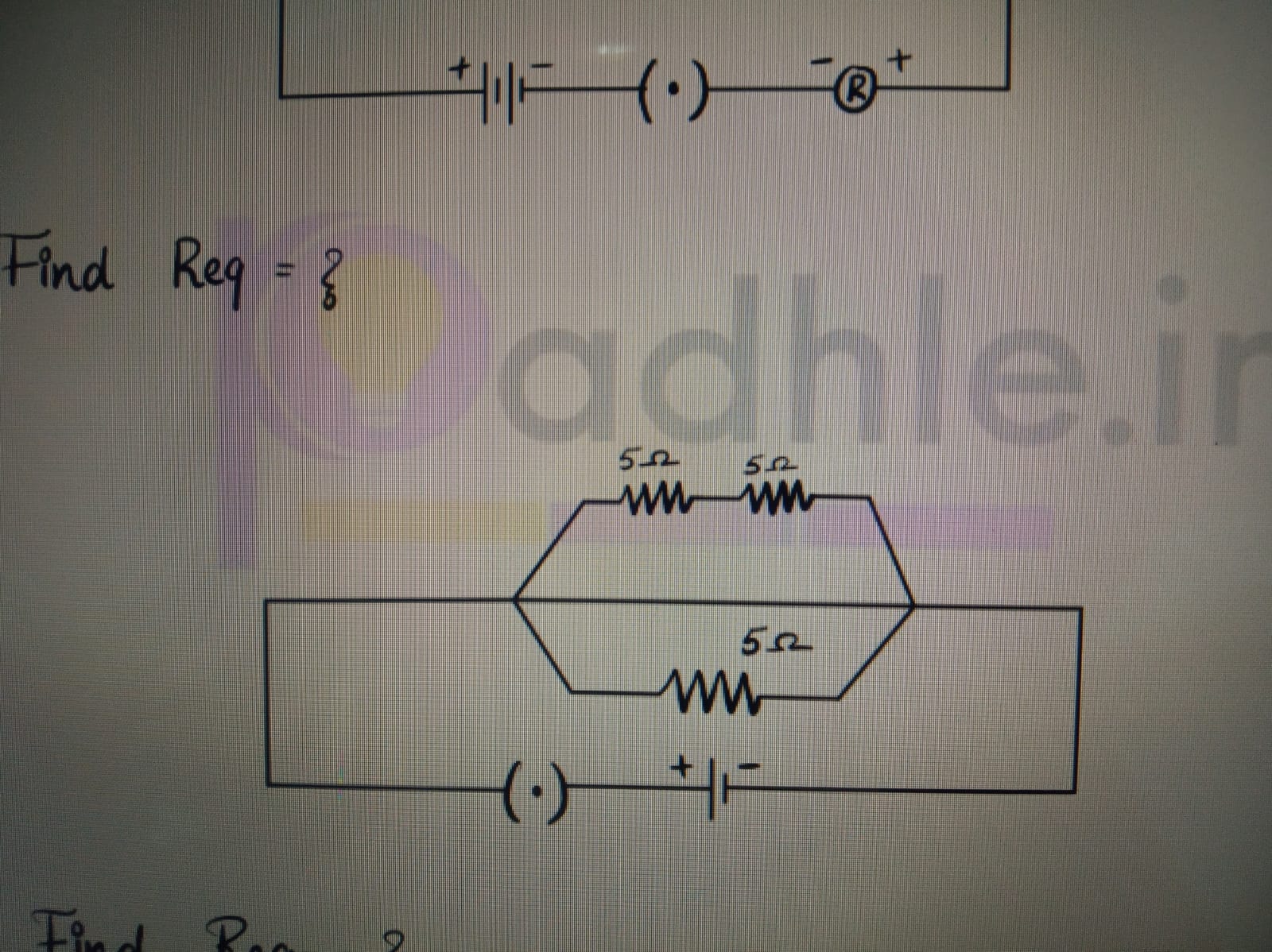
CBSE Class 10 Answered
Define Drift speed. Also we know that the drift speed of a steady current carrying conductor is about 1mm/s. Then how we observe lightening fast speed of current in a typical circuit?
Asked by Akshit Wahi | 12 Sep, 2011, 12:00: AM
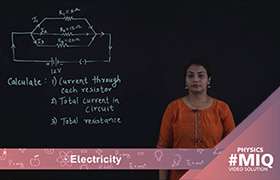
In a conductor, the electrons undergo frequent collisions with the ions of the material. Hence, the direction of the electrons undergoes a random change. See figure below, the net effect is that in addition to the random motion of the electrons, there is also a very slow net motion or drift of the electrons. This drift or flow with a constant velocity (in a direction opposite to  ) is called the drift velocity VD.
) is called the drift velocity VD.
 ) is called the drift velocity VD.
) is called the drift velocity VD.The drift velocity of the electrons Vd is (using E = V / l)

In a circuit, when potential difference is applied, the electrons gets attracted towards the positive terminal and acquire a faster speed.
Answered by | 13 Sep, 2011, 10:34: AM
Application Videos
Concept Videos
CBSE 10 - Physics
Asked by khajannirwan | 27 Feb, 2024, 10:20: PM
CBSE 10 - Physics
Asked by saanviyadla | 24 Jan, 2024, 07:06: PM
CBSE 10 - Physics
Asked by kamalaranjanmohantymohanty5 | 06 Jan, 2024, 10:05: AM
CBSE 10 - Physics
Asked by nandhikasugumar | 05 Oct, 2023, 04:01: PM
CBSE 10 - Physics
Asked by daniya062008 | 02 Oct, 2023, 08:25: PM
CBSE 10 - Physics
Asked by prassanna.j | 03 Sep, 2023, 12:28: PM
CBSE 10 - Physics
Asked by prassanna.j | 03 Sep, 2023, 12:21: PM
CBSE 10 - Physics
Asked by prassanna.j | 03 Sep, 2023, 12:13: PM
CBSE 10 - Physics
Asked by prassanna.j | 03 Sep, 2023, 12:11: PM