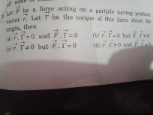CBSE Class 11-science Answered
A rigid body in mechanical equilibrium is undergoing neither linear nor rotational acceleration; however it could be translating or rotating at a constant velocity.---could not quite understand this.. can u please xplain?
Asked by nilanjana lodh | 20 May, 2011, 07:11: AM
The necessary conditions for mechanical equilibrium for a system of particles are:
- (i)The vector sum of all external forces is zero;
- (ii) The sum of the moments of all external forces about any line is zero.
- A rigid body is in mechanical equilibrium when the sum of all forces on all particles of the system is zero, and also the sum of all torques on all particles of the system is zero.
A rigid body in mechanical equilibrium is undergoing neither linear nor rotational acceleration; however it could be translating or rotating at a constant velocity.
Therefore for linear or rotational acceleration we required a net force whereas for translating or rotating at a constant velocity,we don't required a net force.
Answered by | 20 May, 2011, 01:58: AM
Concept Videos
CBSE 11-science - Physics
Asked by rustampathan | 25 Feb, 2024, 06:39: PM
CBSE 11-science - Physics
Asked by gipaalsy | 08 Feb, 2024, 05:41: AM
CBSE 11-science - Physics
Asked by priyankaprajapti81 | 04 Nov, 2023, 10:47: PM
CBSE 11-science - Physics
Asked by gdeadshot85 | 14 Jan, 2023, 09:58: PM
CBSE 11-science - Physics
Asked by devanshchauhan325 | 23 Dec, 2022, 07:34: AM
CBSE 11-science - Physics
Asked by koushtubhroy | 20 Dec, 2022, 07:36: AM
CBSE 11-science - Physics
Asked by pushpakumari291279 | 20 Aug, 2022, 08:15: AM
CBSE 11-science - Physics
Asked by adipadmakarri | 26 Sep, 2021, 06:08: PM
CBSE 11-science - Physics
Asked by adipadmakarri | 25 Sep, 2021, 11:18: AM